Paper: Systematic attribution of heatwaves to the emissions of carbon majors
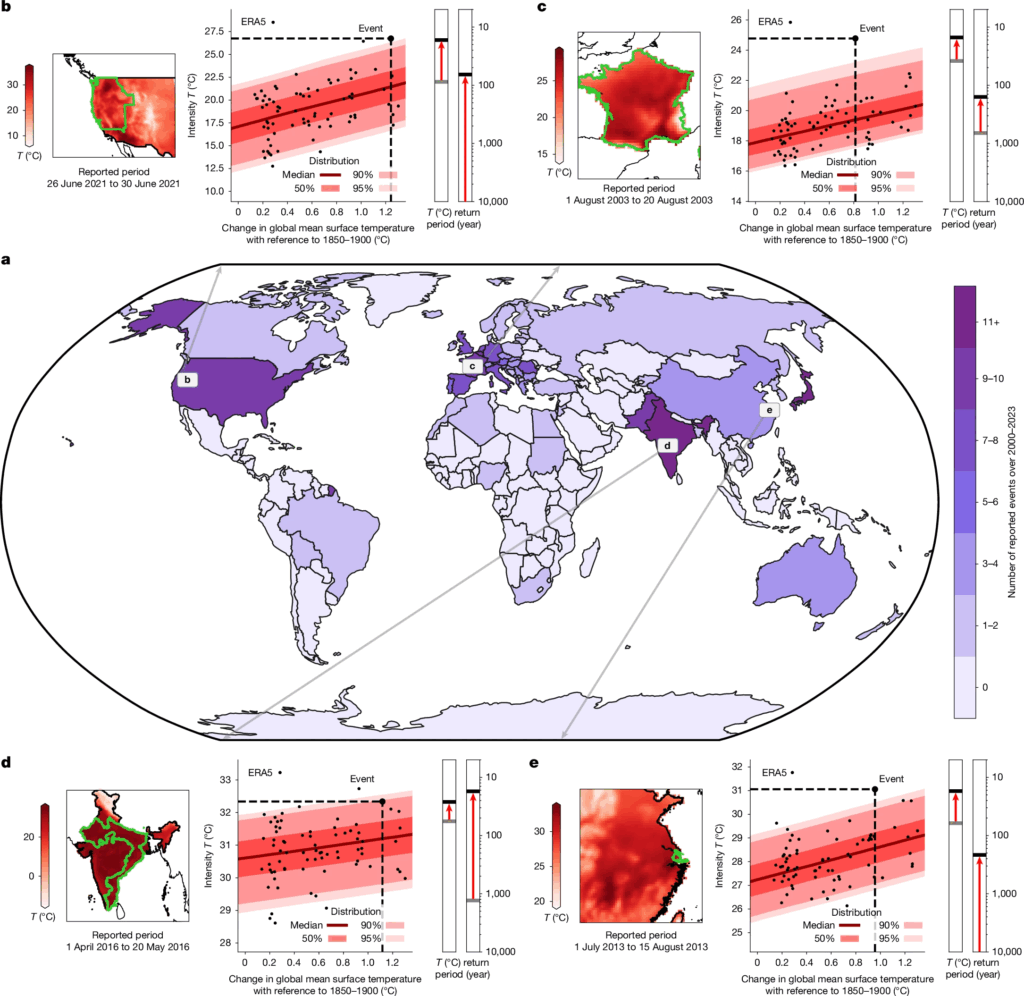
« Researchers analysed the emissions that were facilitated by the 180 largest producers of fossil fuels and cement – referred to in the study as “carbon majors”. The emissions from these carbon majors account for 60 percent of humanity’s total cumulative CO2 emissions from 1850 to 2023, with the rest of the CO2 emissions largely attributable to land use activities. The researchers then calculated the contribution of each carbon major to the change in global average temperature. »
Paper: The concept of spectrally nudged storylines for extreme event attribution
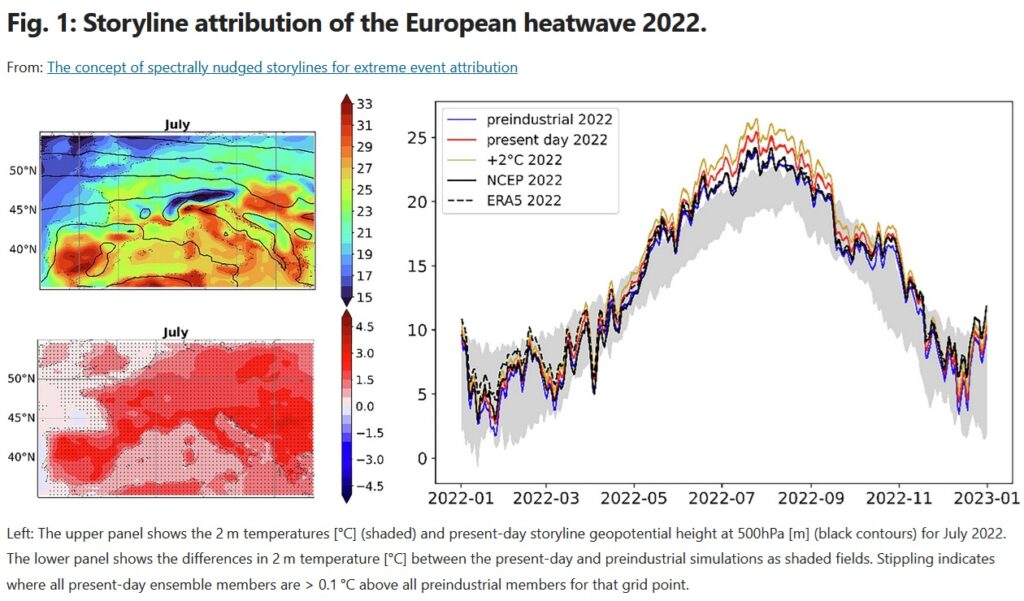
Read the paper: The concept of spectrally nudged storylines for extreme event attribution.
» (…) Spectrally nudged storylines thus offer a new, easily implemented and easily understandable way of communicating climate change to the general public and decision-makers, as well as a pathway for detailed attribution of climate impacts. The technique offers great potential as an addition to the established attribution methods by answering different questions and providing new attribution results. »
A collaboration between XAIDA and CLINT EU projects.
Paper: One third of the Global soybean production failure in 2012 is attributable to climate change
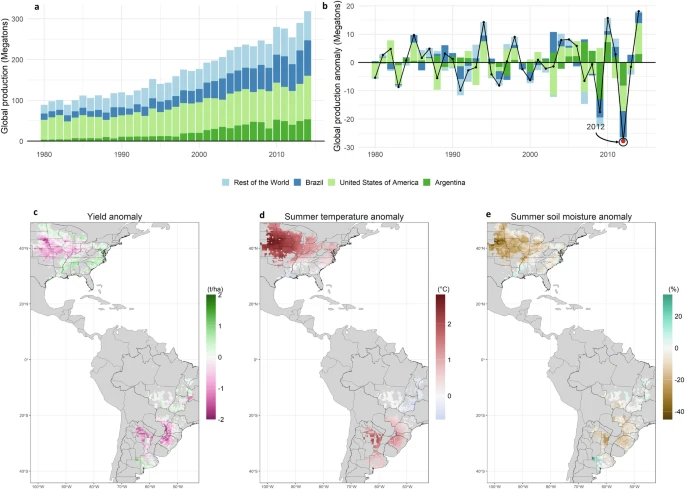
Read the paper: In 2012, soybean crops failed in the three largest producing regions due to spatially compounded hot and dry weather across North and South America. Here, we present different impact storylines of the 2012 event, calculated by combining a statistical crop model with climate model simulations of 2012 conditions under pre-industrial, present-day (+1 °C), and future (+2 °C) conditions. These simulations use the ECHAM6 climate model and maintain the same observed seasonally evolving atmospheric circulation. Our results demonstrate that anthropogenic warming strongly amplifies the impacts of such a large-scale circulation pattern on global soybean production. Although the drought intensity is similar under different warming levels, larger crop losses are driven not only by warmer temperatures but also by stronger heat-moisture interactions. We estimate that one-third of the global soybean production deficit in 2012 is attributable to anthropogenic climate change. Future warming (+2 °C above pre-industrial) would further exacerbate production deficits by one-half compared to present-day 2012 conditions. This highlights the increasing intensity of global soybean production shocks with warming, requiring urgent adaptation strategies.
Paper: Artificial intelligence for modeling and understanding extreme weather and climate events
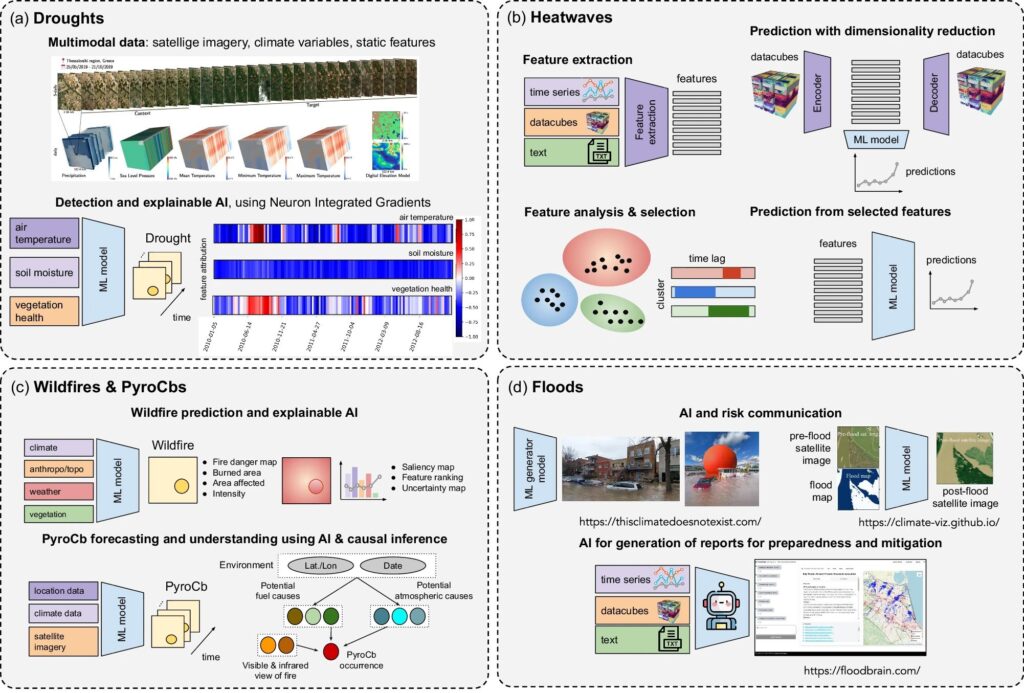
Read the paper: Artificial intelligence for modeling and understanding extreme weather and climate events
» In recent years, artificial intelligence (AI) has deeply impacted various fields, including Earth system sciences, by improving weather forecasting, model emulation, parameter estimation, and the prediction of extreme events. The latter comes with specific challenges, such as developing accurate predictors from noisy, heterogeneous, small sample sizes and data with limited annotations. This paper reviews how AI is being used to analyze extreme climate events (like floods, droughts, wildfires, and heatwaves), highlighting the importance of creating accurate, transparent, and reliable AI models. (…) »
A collaboration between XAIDA and CLINT EU projects but also USMILE, AI4PEX, ELIAS, MeDiTwin, DeepCube and several national programmes.
Paper: Generative networks for spatio-temporal gap filling of Sentinel-2 reflectances
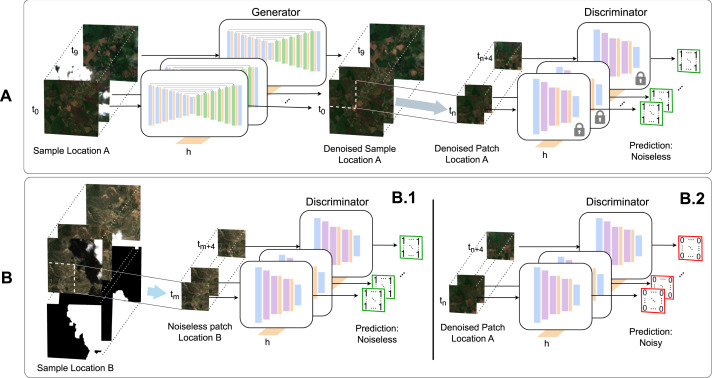
Read the paper: Generative networks for spatio-temporal gap filling of Sentinel-2 reflectances
« Earth observation from satellite sensors offers the possibility to monitor natural ecosystems by deriving spatially explicit and temporally resolved biogeophysical parameters. Optical remote sensing, however, suffers from missing data mainly due to the presence of clouds, sensor malfunctioning, and atmospheric conditions. This study proposes a novel deep learning architecture to address gap filling of satellite reflectances, more precisely the visible and near-infrared bands, and illustrates its performance at high-resolution Sentinel-2 data. (…) »
Paper: How to spend money from the climate loss and damage fund fairly and quickly

Read the paper: How to spend money from the climate loss and damage fund fairly and quickly.
Floods, heat and droughts hit developing countries disproportionately. How to compensate for climate damage in these countries in a fair way ? A group of scientists…
Paper: Summer wind patterns in the north are changing due to climate change
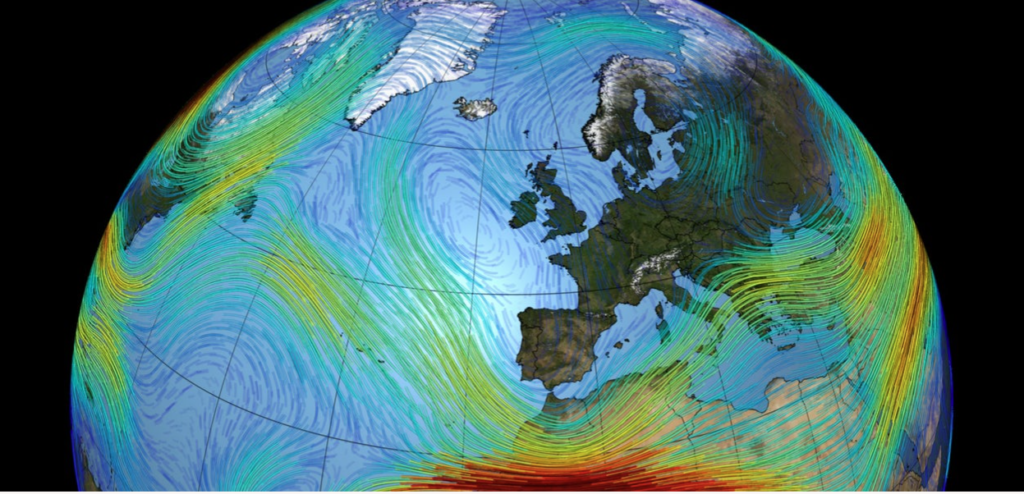
Read the paper: Summer wind patterns in the north are changing due to climate change. The emissions of greenhouse gases and aerosols have led to a weakening of weather systems in the summer on the Northern Hemisphere.
Paper: Severe storms in France have already been intensified by climate change
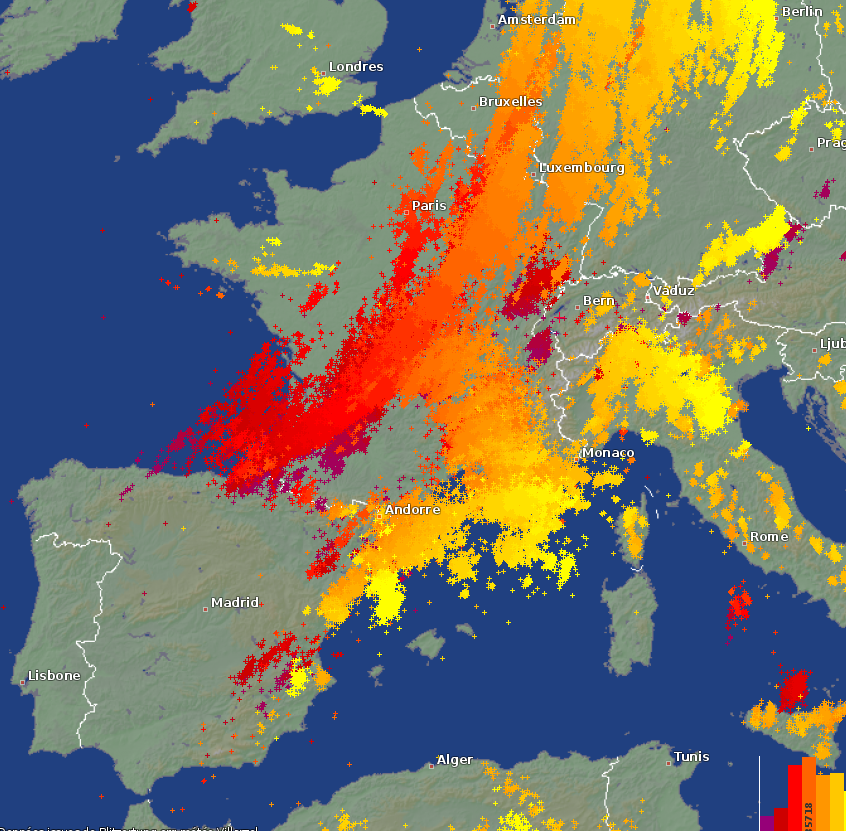
Read the paper: Severe thunderstorms, such as derechos, are less studied phenomena in Europe than in the USA. However, a recent event has highlighted the very real threat they can pose to Europeans.
Paper: Simulations of a worst-case heatwave during the Paris Olympics in 2024

Read the paper: The Paris Olympics in 2024 will take place between July 26th to August 11th 2024, at the apex of the temperature seasonal cycle. Can the deadly 15-day temperature record of 2003 be broken in the present decades? How hot can it be in the Paris area?
Paper: Attributing Venice Acqua Alta events to a changing climate and evaluating the efficacy of MoSE adaptation strategy
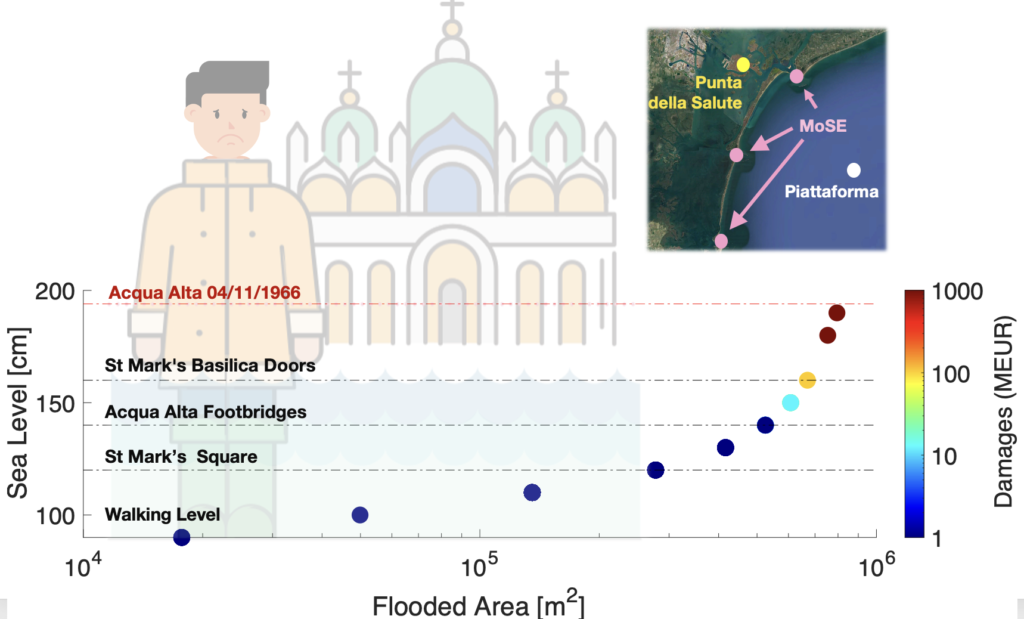
Read the paper: This research employs an innovative approach by utilizing analogues of atmospheric patterns to scrutinize four notable Acqua Alta events in the Venice lagoon, specifically those connected with intense Mediterranean cyclones that transpired in 1966, 2008, 2018, and 2019. The findings provide compelling evidence that modifications in atmospheric circulation, while not solely attributable to human activities, are undeniably linked to the increased severity of these events, thereby illuminating the vulnerability of Venice to the impacts of climate change. Furthermore, the study conducts a comprehensive assessment of the MoSE system, a crucial adaptation infrastructure designed to mitigate flooding in Venice, and underscores its effectiveness in protecting the city against events with historical analogues, particularly those akin to the catastrophic 1966 flood.
