eXtreme events : Artificial Intelligence for Detection and Attribution
Seventeen European research institutes are joining forces with climate risk practitioners to better assess and predict the influence of climate change on extreme weather using novel artificial intelligence methods. This new EU-funded 4-year project, called “XAIDA”, started in September 2021.
In 2021, Geert Jan van Oldenborgh, one of the initiators of XAIDA, passed away. He also laid down the foundations of rapid attribution.


Extreme Events
News
Climate Extremes & Societal Risks
For this final event together with the MYRIAD project, XAIDA chose to focus on Climate Extremes & Societal Risks. This will take place at Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam on December 17th and 18th. A public event inviteing all partners and stakeholders will take place in the afternoon on December 17th.
Check out the lectures and details.
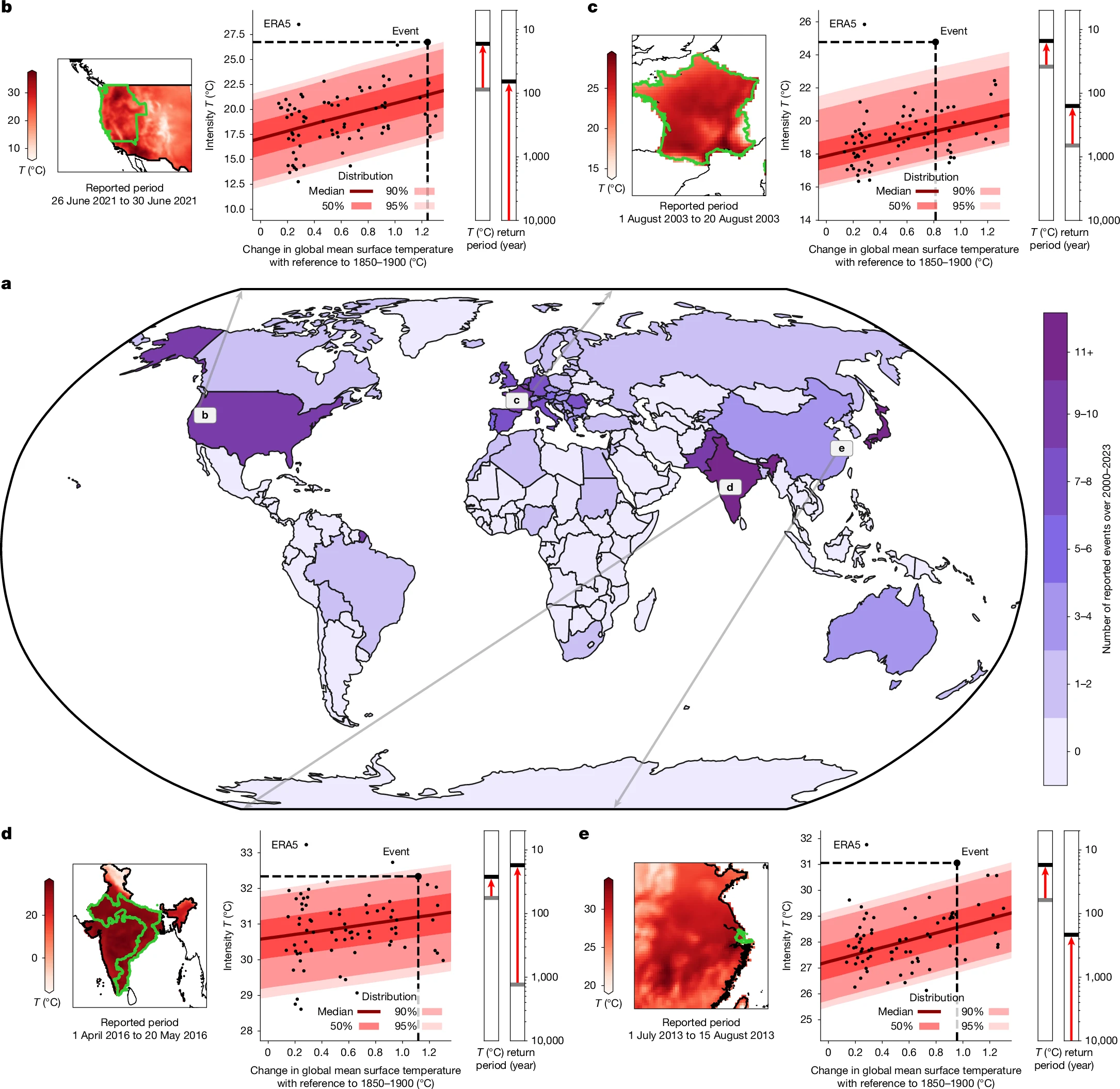
Paper: Systematic attribution of heatwaves to the emissions of carbon majors
« Researchers analysed the emissions that were facilitated by the 180 largest producers of fossil fuels and cement – referred to in the study as “carbon majors”. The emissions from these carbon majors account for 60 percent of humanity’s total cumulative CO2 emissions from 1850 to 2023, with the rest of the CO2 emissions largely attributable to land use activities. The researchers then calculated the contribution of each carbon major to the change in global average temperature. »
Teaching Material: Why are football pitches flooding?
XAIDA is collaborating with the PSTT (Primary Science Teaching Trusts) collaborators. PSTT produces some teaching material based on XAIDA work.
This work is based on the attribution work led by several of XAIDA scientists conducted with the World Weather Attribution (WWA).
Read more on Attribution of Extreme Weather Event!
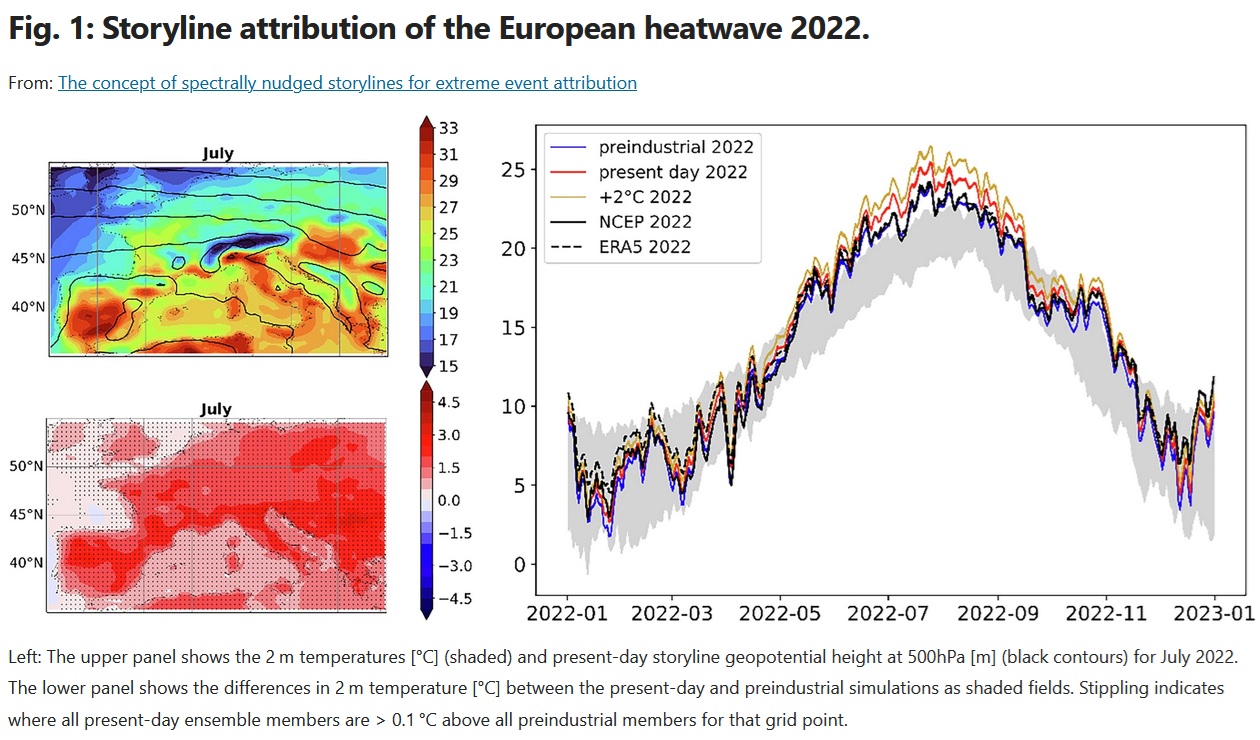
Paper: The concept of spectrally nudged storylines for extreme event attribution
Read the paper: The concept of spectrally nudged storylines for extreme event attribution.
» (…) Spectrally nudged storylines thus offer a new, easily implemented and easily understandable way of communicating climate change to the general public and decision-makers, as well as a pathway for detailed attribution of climate impacts. The technique offers great potential as an addition to the established attribution methods by answering different questions and providing new attribution results. »
A collaboration between XAIDA and CLINT EU projects.
Teaching Materials: Videos on Extreme Events for Primary Students
XAIDA’s partner Office for Climate Education (OCE) worked on Teaching Materials including here a video series.
The ‘CLIM’ series, developed by the Office for Climate Education in collaboration with XAIDA researchers focuse on extreme weather phenomena.
Read and wathc more!
XAIDA Webinar #18
The 18th session of our webinar will occur on June 10th, 2025 at 10AM (10:00) CET. During this webinar Dr. Pradeebane Vaittinada Ayar will discuss his work on ‘Ensemble Random Forest for Tropical Cyclone Tracking’.
‘Even though tropical cyclones (TCs) are well documented during the intense part of their lifecycle until they start to evanesce, many physical and statistical properties governing them are not well captured by gridded reanalysis or simulated by Earth system models. Thus, the tracking of TCs remains a matter of interest for the investigation of observed and simulated tropical cyclones. Two types of cyclone tracking schemes are available. On the one hand, some trackers rely on physical and dynamical properties of the TCs and user-prescribed thresholds, which make them rigid. They need numerous variables that are not always available in the models.
On the other hand, trackers are leaning on deep learning, which, by nature, needs large amounts of data and computing power.’
Check out the details to attend and follow the discussion!